The motherboard is a multilayer sheet of printed circuit board that contains the copper conductor rails that connect the motherboard's components to one another.
The motherboard and the connected devices are mounted inside the computer case with the power supply and cooling system to form the computer chassis.
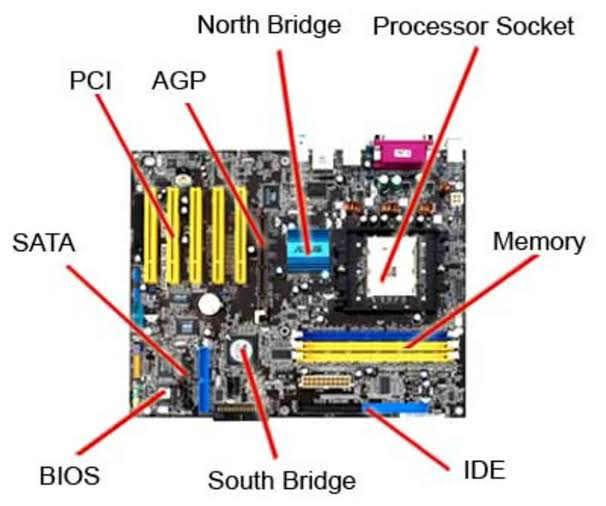
Components of a computer motherboard

- CMOS battery

The battery on the motherboard provides an autonomous power supply for the BIOS after the computer is turned off. Otherwise, the date, time, and BIOS settings will not be saved. In some cases, the computer may not start.
Motherboard has a slot designed to hold one of three types of batteries:
- CR2032 has a capacity of 210-230 mAh;
- CR2025 has a capacity of 150 mAh;
- CR2016 has a capacity of 75-90 mAh.
The voltage of these batteries is 3 V.
The first two letters occurring in the designation define the composition of the battery:
CR is lithium.
The first 2 digits are the diameter in millimeters, the second 2 digits are the thickness in tenths of a millimeter.
A smaller battery can be installed on the laptop's motherboard - for example, CR 1220.
- The F_USB1 and F_USB2 connectors are used for the USB ports.

Each USB connector on the motherboard supports the connection of two USB ports on the computer chassis.
- PCI express x16 and PCI express x4.

These are the connectors for connecting video cards.
- PCI 1, PCI 2 are universal and more obsolete connectors.

Sound cards, network cards, and other expansion cards can be plugged into these slots.
- TPM connector is a connector to install a TPM cryptoprocessor, which stores cryptographic keys for data protection.

- PCIE X 1_1 connector, PCIEX 1_2 connector, PCIEX 1_3 connector.

These are modern high-speed connectors with a smaller size. They connect sound cards, TV tuners, network cards, and many different expansion cards.
- COM connector is a serial port.

This port allows you to connect your computer to an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), satellite receivers, and cash registers. Also, using this port, you can connect two computers into one network.
- Front panel audio connector

This connector on the motherboard supports the connection of headphones, speakers, or a microphone to the computer chassis.
- Bus controllers (microcontrollers) are designed to control electronic devices.

- CPU_ FAN, SYS_FAN1, SYS_FAN2, SYS_FAN3 connectors.

They are used to connect the fans of the cooling system.
- Connectors for external peripherals such as keyboard, mouse, speakers, etc.

- ATX_12V connector.

This is an additional eight-pin connector. It is needed for duplicating wires in case of high current consumption by the processor to take the load off the main ATX connector (18).
The 13, 14, 15 elements represent a unified system of power supply unit.
- MOSFET Transistors.

These transistors make up the VRM voltage regulator module, which controls how much voltage is delivered to components on the motherboard, such as the CPU or graphics card.
- The chokes create the necessary inductance.

- The capacitors provide the necessary capacitance.

They absorb the pulses from the power supply to the motherboard socket.
- CPU socket.

A socket is a slot on the motherboard where the processor is installed. The socket type is the most important specification of the computer. It determines the list of compatible chipsets, processors, motherboards, and cooling systems.
Sockets vary in the number of pins, which usually increases with the power and complexity of the processors.
You should consider the type of socket when choosing a motherboard. Technically, sockets can vary from each other by the availability of additional controllers, performance, and the ability to support the integrated graphics core of the processor.
It is important to remember that if you choose a relatively outdated socket, you cannot upgrade your computer by installing a new processor. When buying a motherboard, it is necessary to study the socket installed in it and the processors supported by this socket.
- DIMM memory card slots.

- ATX Connector for power supply unit.

- Slot M.2. This slot allows you to connect an SSD. MSATS Signature stands for Plug-in SSD Form Factor.

- Southbridge or chipset. This is located under the heatsink.

It ensures the proper operation of all other devices that are included in the motherboard.
- The B_BIOS and M_BIOS chips are Dual Bios.

M_Bios is the primary microchip. B_Bios is the reserve one if the M_Bios chip fails to update or delete the Bios system.
22 and 23 are SATA 2 (blue) and SATA 3 (white) connectors.

They are dedicated to connect hard drives, CD, DVD drives, and SSD drives. The SATA 2 connector supports speeds up to 3 Gbit/s. The SATA 3 connector is more advanced, as it supports speeds up to 6 Gbit/s.
Chipset
A chipset is a series of chips on the motherboard that ensures the connection between the processor and the peripherals of the system (RAM, storage, USB ports, etc.). The ability to overclock the CPU in many ways depends on the chipset. This chipset is classified as one of the system's most important components. It determines the system's performance, expandability, stability under different settings and conditions, upgrades, etc.

- Central processor
- Clock generator
- Bus
- Chipset
- Northbridge. In modern computers, integrated into the CPU.
- High-speed PCI-Express or AGP bus.
- Graphics adapter slot
- Memory bus
- Memory slots
- Internal bus
- Southbridge
- PCI bus
- PCI slots
- Motherboard connectors
- LPC bus
- BIOS
- Super I/O controller.
Form Factor
Form factor is defined as a standard that determines the size of the motherboard for a computer case, which matches one of the three commonly used formats: ATX (1), Micro-ATX (2), Mini-ITX (3).

Dimensions: ATX 305x244 mm; Micro ATX 244x244 mm; Mini ITX 170x170 mm.
Smaller boards allow you to reduce the size of the computer chassis. On these boards, all the elements are mounted close to each other. However, this increases the temperature of the computer case and doesn't allow to make a lot of connectors.
The motherboard form factor that is appropriate for the specific case is listed on the motherboard manufacturer's websites.




No comments:
Post a Comment